- nrThe number of layers in the radial direction
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:The number of layers in the radial direction
- rmaxOuter radius
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Outer radius
- vertical_axisThe vertical axis about which to compute the radial coordinate (x, y, or z)
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The vertical axis about which to compute the radial coordinate (x, y, or z)
RadialBin
Creates spatial bins for layers in the radial direction
Description
This user object bins the spatial domain according to layers in the radial direction. The vertical direction (about which the radial coordinate is computed) is specified with the vertical_axis parameter. Non-uniform layer sizes can be specified by setting growth_r greater than unity (layers grow in size in increasing radial coordinate) or growth_r less than unity (layers shrink in size in increasing radial coordinate).
For defining bins in an annular radial coordinate system, set rmin to the inner radial coordinate.
To help with debugging, you can visualize this user object (i.e., the bin indices) using a SpatialUserObjectAux.
Example Input Syntax
Below is an example input file that constructs layered bins in the radial direction with uniform, radially increasing, or radially decreasing layer widths.
[UserObjects<<<{"href": "../../syntax/UserObjects/index.html"}>>>]
[uniform_bins]
type = RadialBin<<<{"description": "Creates spatial bins for layers in the radial direction", "href": "RadialBin.html"}>>>
rmin<<<{"description": "Inner radius. Setting 'rmin = 0' corresponds to a cross-section of a circle"}>>> = 0.0
rmax<<<{"description": "Outer radius"}>>> = 1.5
nr<<<{"description": "The number of layers in the radial direction"}>>> = 10
vertical_axis<<<{"description": "The vertical axis about which to compute the radial coordinate (x, y, or z)"}>>> = z
[]
[growing_bins]
type = RadialBin<<<{"description": "Creates spatial bins for layers in the radial direction", "href": "RadialBin.html"}>>>
rmin<<<{"description": "Inner radius. Setting 'rmin = 0' corresponds to a cross-section of a circle"}>>> = 0.0
rmax<<<{"description": "Outer radius"}>>> = 1.5
nr<<<{"description": "The number of layers in the radial direction"}>>> = 10
growth_r<<<{"description": "The ratio of radial sizes of successive rings of elements"}>>> = 1.2
vertical_axis<<<{"description": "The vertical axis about which to compute the radial coordinate (x, y, or z)"}>>> = z
[]
[shrinking_bins]
type = RadialBin<<<{"description": "Creates spatial bins for layers in the radial direction", "href": "RadialBin.html"}>>>
rmin<<<{"description": "Inner radius. Setting 'rmin = 0' corresponds to a cross-section of a circle"}>>> = 0.0
rmax<<<{"description": "Outer radius"}>>> = 1.5
nr<<<{"description": "The number of layers in the radial direction"}>>> = 10
growth_r<<<{"description": "The ratio of radial sizes of successive rings of elements"}>>> = 0.8
vertical_axis<<<{"description": "The vertical axis about which to compute the radial coordinate (x, y, or z)"}>>> = z
[]
[]The bins for radially decreasing layer widths are shown below, colored by bin ID.
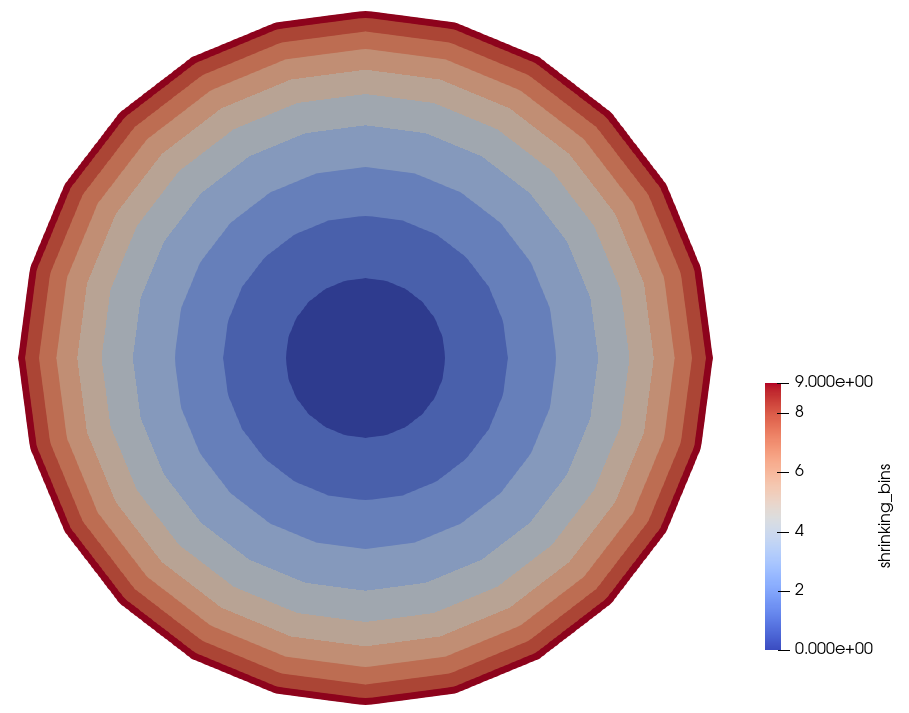
Figure 1: Radial bin indices for shrinking layer widths
Input Parameters
- growth_r1The ratio of radial sizes of successive rings of elements
Default:1
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:The ratio of radial sizes of successive rings of elements
- rmin0Inner radius. Setting 'rmin = 0' corresponds to a cross-section of a circle
Default:0
C++ Type:double
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:Inner radius. Setting 'rmin = 0' corresponds to a cross-section of a circle
Optional Parameters
- allow_duplicate_execution_on_initialFalseIn the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:In the case where this UserObject is depended upon by an initial condition, allow it to be executed twice during the initial setup (once before the IC and again after mesh adaptivity (if applicable).
- execute_onTIMESTEP_ENDThe list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
Default:TIMESTEP_END
C++ Type:ExecFlagEnum
Controllable:No
Description:The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html.
- execution_order_group0Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
Default:0
C++ Type:int
Controllable:No
Description:Execution order groups are executed in increasing order (e.g., the lowest number is executed first). Note that negative group numbers may be used to execute groups before the default (0) group. Please refer to the user object documentation for ordering of user object execution within a group.
- force_postauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in POSTAUX
- force_preauxFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREAUX
- force_preicFalseForces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Forces the UserObject to be executed in PREIC during initial setup
Execution Scheduling Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- use_displaced_meshFalseWhether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Advanced Parameters
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Unit:(no unit assumed)
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- use_interpolated_stateFalseFor the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:For the old and older state use projected material properties interpolated at the quadrature points. To set up projection use the ProjectedStatefulMaterialStorageAction.