Beams
Small strain Timoshenko beam bending
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 0.554 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 0.0142 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 2.6 N/, poisson's ratio of 0.3, shear modulus of 1 N/ and shear coefficient of 0.85. A point load of magnitude 110 N is applied at the free end of the cantilever beam in Y-direction.
# Test for small strain timoshenko beam bending in y direction
# A unit load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 2.60072400269
# Shear modulus (G) = 1.00027846257
# Poisson's ratio (nu) = 0.3
# Shear coefficient (k) = 0.85
# Cross-section area (A) = 0.554256
# Iy = 0.0141889 = Iz
# Length = 4 m
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 204.3734
# The small deformation analytical deflection of the beam is given by
# delta = PL^3/3EI * (1 + 3.0 / alpha) = 5.868e-4 m
# Using 10 elements to discretize the beam element, the FEM solution is 5.852e-2m.
# This deflection matches the FEM solution given in Prathap and Bhashyam (1982).
# References:
# Prathap and Bhashyam (1982), International journal for numerical methods in engineering, vol. 18, 195-210.
# Note that the force is scaled by 1e-4 compared to the reference problem.
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 1
nx = 10
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 4.0
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = ConstantRate<<<{"description": "Computes residual or the rate in a simple ODE of du/dt = rate.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/ConstantRate.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
rate<<<{"description": "The constant rate in 'du/dt = rate'"}>>> = 1.0e-4
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
line_search = 'none'
nl_max_its = 15
nl_rel_tol = 1e-10
nl_abs_tol = 1e-10
dt = 1
dtmin = 1
end_time = 2
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 2.60072400269
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.3
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.85
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.554256
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0141889
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0141889
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]Results
For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha is given by: The value of alpha is not high enough for the beam to behave like a thin beam where shear effects are not significant. Hence, the shear effects are considered and the small deformation analytical deflection of a cantilever beam is given by:
The deflection obtained from MOOSE using 10 elements is 5.85210 m shown in Figure 1.
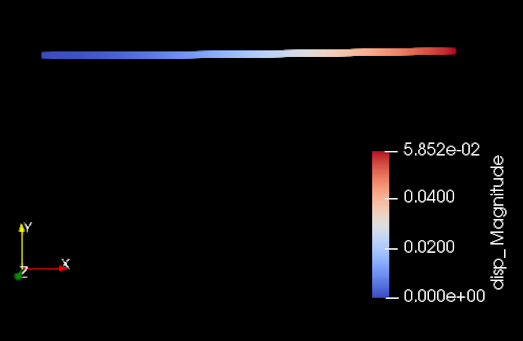
Figure 1: Displacement of the Timoshenko beam in bending.
Small strain Euler beam bending
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 0.554 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 0.0142 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 2.6 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, shear modulus of 110 N/ and shear coefficient of 0.85. A point load of magnitude 110 N is applied at the free end of the cantilever beam in Y-direction.
# Test for small strain Euler beam bending in y direction
# A unit load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 2.60072400269
# Shear modulus (G) = 1.0e4
# Poisson's ratio (nu) = -0.9998699638
# Shear coefficient (k) = 0.85
# Cross-section area (A) = 0.554256
# Iy = 0.0141889 = Iz
# Length = 4 m
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 2.04e6
# The small deformation analytical deflection of the beam is given by
# delta = PL^3/3EI * (1 + 3.0 / alpha) = PL^3/3EI = 5.78e-2 m
# Using 10 elements to discretize the beam element, the FEM solution is 5.766e-2 m.
# The ratio beam FEM solution and analytical solution is 0.998.
# References:
# Prathap and Bhashyam (1982), International journal for numerical methods in engineering, vol. 18, 195-210.
# Note that the force is scaled by 1e-4 compared to the reference problem.
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 1
nx = 10
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 4.0
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = ConstantRate<<<{"description": "Computes residual or the rate in a simple ODE of du/dt = rate.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/ConstantRate.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
rate<<<{"description": "The constant rate in 'du/dt = rate'"}>>> = 1.0e-4
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
line_search = 'none'
nl_max_its = 15
nl_rel_tol = 1e-10
nl_abs_tol = 1e-10
dt = 1
dtmin = 1
end_time = 2
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 2.60072400269
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = -0.9998699638
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.85
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.554256
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0141889
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0141889
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]Results
For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha is given by: Since the value of alpha is quite high, the beam behaves like a thin beam where shear effects are not significant. Hence, the small deformation analytical deflection of a cantilever beam is given by:
The deflection obtained from MOOSE using 10 elements is 5.76610 m shown in Figure 2. The ratio beam FEM solution and analytical solution is 0.998.
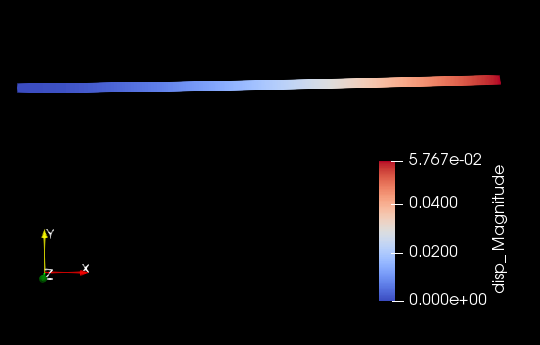
Figure 2: Displacement of the Euler beam in bending.
Small strain Euler beam axial loading
A pipe 5 feet (60 inches) long having an internal diameter of 8 inches and outer diameter of 10 inches is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The Young's modulus of elasticity of the pipe is 3010 lb/, the shear modulus is 11.5410 lb/ and poisson's ratio is 0.3. The pipe is fixed at one end and an axial load of 50000 lb is applied at the other end.
# Test for small strain Euler beam axial loading in x direction.
# Modeling a pipe with an OD of 10 inches and ID of 8 inches
# The length of the pipe is 5 feet (60 inches) and E = 30e6
# G = 11.5384615385e6 with nu = 0.3
# The applied axial load is 50000 lb which results in a
# displacement of 3.537e-3 inches at the end
# delta = PL/AE = 50000 * 60 / pi (5^2 - 4^2) * 30e6 = 3.537e-3
# In this analysis the applied force is used as a BC
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 1
nx = 10
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 60.0
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[force_x2]
type = ConstantRate<<<{"description": "Computes residual or the rate in a simple ODE of du/dt = rate.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/ConstantRate.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
rate<<<{"description": "The constant rate in 'du/dt = rate'"}>>> = 50000.0
[]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = PJFNK
line_search = 'none'
nl_max_its = 15
nl_rel_tol = 1e-10
nl_abs_tol = 1e-8
dt = 1
dtmin = 1
end_time = 2
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[]
[solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[]
[solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[]
[solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[]
[solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[]
[solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[forces_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = CONSTANT
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = MONOMIAL
[]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[forces_x]
type = MaterialRealVectorValueAux<<<{"description": "Capture a component of a vector material property in an auxiliary variable.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/MaterialRealVectorValueAux.html"}>>>
property<<<{"description": "The material property name."}>>> = forces
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = forces_x
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 30e6
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.3
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[]
[strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 28.274
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[]
[stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '60.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[]
[disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '60.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[]
[forces_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '60.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = forces_x
[]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
[]Results
The analytical displacement at the end is given by:
The displacement at the end obtained from the MOOSE using 10 elements is 3.53710 in as shown in Figure 3.
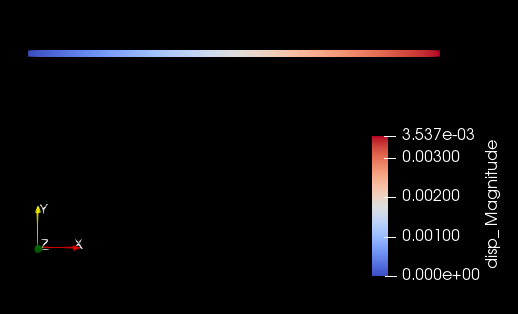
Figure 3: Displacement of the Euler beam under axial load.
Large strain/large rotation of cantilever beam
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 1 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 0.16 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 110 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, shear modulus of 110 N/ and shear coefficient of 1. A point load of magnitude 300 N is applied at the free end of the cantilever beam in Y-direction.
# Large strain/large rotation cantilever beam test
# A 300 N point load is applied at the end of a 4 m long cantilever beam.
# Young's modulus (E) = 1e4
# Shear modulus (G) = 1e8
# shear coefficient (k) = 1.0
# Poisson's ratio (nu) = -0.99995
# Area (A) = 1.0
# Iy = Iz = 0.16
# The dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 1e6
# Since the value of alpha is quite high, the beam behaves like
# a thin beam where shear effects are not significant.
# Beam deflection:
# small strain+rot = 3.998 m (exact 4.0)
# large strain + small rotation = -0.05 m in x and 3.74 m in y
# large rotations + small strain = -0.92 m in x and 2.38 m in y
# large rotations + large strain = -0.954 m in x and 2.37 m in y (exact -1.0 m in x and 2.4 m in y)
# References:
# K. E. Bisshopp and D.C. Drucker, Quaterly of Applied Mathematics, Vol 3, No. 3, 1945.
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = FileMesh
file = beam_finite_rot_test_2.e
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 1
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel<<<{"description": "Residual contribution to an ODE from a source functor acting at nodes.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = 2
functor<<<{"description": "The forcing functor. A functor is any of the following: a variable, a functor material property, a function, a postprocessor or a number."}>>> = force
[../]
[]
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[./force]
type = PiecewiseLinear<<<{"description": "Linearly interpolates between pairs of x-y data", "href": "../../source/functions/PiecewiseLinear.html"}>>>
x<<<{"description": "The abscissa values"}>>> = '0.0 2.0 8.0'
y<<<{"description": "The ordinate values"}>>> = '0.0 300.0 300.0'
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = PJFNK
line_search = 'none'
petsc_options = '-snes_ksp_ew'
petsc_options_iname = '-ksp_gmres_restart -pc_type -pc_hypre_type -pc_hypre_boomeramg_max_iter'
petsc_options_value = '201 hypre boomeramg 4'
nl_max_its = 50
nl_rel_tol = 1e-9
nl_abs_tol = 1e-7
l_max_its = 50
dt = 0.05
end_time = 2.1
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1e4
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = -0.99995
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 1
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeFiniteBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a rotation increment for finite rotations of the beam and computes the small/large strain increments in the current rotated configuration of the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeFiniteBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '1'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.16
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.16
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
large_strain<<<{"description": "Set to true if large strain are to be calculated."}>>> = true
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 1
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./rot_z]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]Results
For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha is given by: Since, the value of alpha is quite high, the beam behaves like a thin beam where shear effects are not significant. The analytical solution for the displacements due to large rotations and large strain of the cantilever beam in X and Y direction is -1 m and 2.4 m respectively (BISSHOPP and DRUCKER (1945)).
The displacement at the free end of the cantilever beam obtained from the MOOSE is -0.954 m in X direction as shown in Figure 4 and 2.37 m in Y direction as shown in Figure 5.
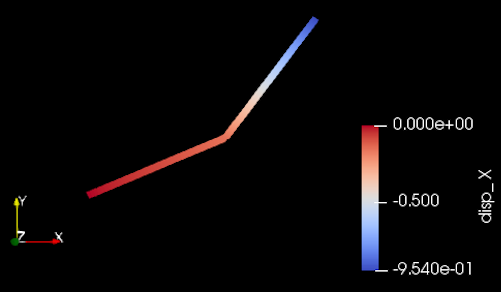
Figure 4: Displacement of the cantilever beam with large strain and rotation in X direction
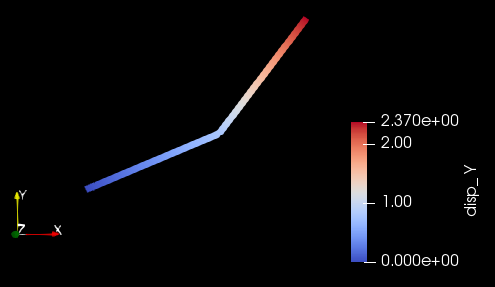
Figure 5: Displacement of the cantilever beam with large strain and rotation in Y direction
Torsion
A 1D cantilever beam of 1 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 0.5 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 110 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 210 N/, poisson's ratio of 0.3 and shear coefficient of 1. A torsion of magnitude 5 N/m is applied at the free end of the cantilever beam.
# Torsion test with automatically calculated Ix
# A beam of length 1 m is fixed at one end and a moment of 5 Nm
# is applied along the axis of the beam.
# G = 7.69e9
# Ix = Iy + Iz = 2e-5
# The axial twist at the free end of the beam is:
# phi = TL/GIx = 3.25e-4
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 1
nx = 10
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 1.0
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Physics<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Physics/index.html"}>>>/SolidMechanics<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Physics/SolidMechanics/index.html"}>>>/LineElement<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Physics/SolidMechanics/LineElement/index.html"}>>>/QuasiStatic<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Physics/SolidMechanics/LineElement/QuasiStatic/index.html"}>>>]
[./block_all]
add_variables<<<{"description": "Add the displacement variables for truss elements and both displacement and rotation variables for beam elements."}>>> = true
displacements<<<{"description": "The nonlinear displacement variables for the problem"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
# Geometry parameters
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.5
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1e-5
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1e-5
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along which Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
block<<<{"description": "The list of ids of the blocks (subdomain) that the stress divergence, inertia kernels and materials will be applied to"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = ConstantRate<<<{"description": "Computes residual or the rate in a simple ODE of du/dt = rate.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/ConstantRate.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
rate<<<{"description": "The constant rate in 'du/dt = rate'"}>>> = 5.0
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = PJFNK
line_search = 'none'
nl_max_its = 15
nl_rel_tol = 1e-10
nl_abs_tol = 1e-8
dt = 1
dtmin = 1
end_time = 2
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 2.0e9
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.3
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '1.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
[]Results
The analytical solution for the axial twist at the free end of the beam is given by:
The rotation at the free end of the beam obtained in MOOSE is 3.210 rad, as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Rotation of the beam due to torsion.
Small strain Euler beam vibration
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 0.01 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 110 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 110 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, density of 1 kg/, shear modulus of 410 N/ and shear coefficient of 1. An impulse load with a peak value of 0.01 N at 0.05 s, as shown in Figure 7, is applied at the free end of the beam in Y direction. The Newmark time integration parameters used in the problem correspond to the Newmark's average acceleration method, i.e., beta=0.25 and gamma=0.5.
Figure 7: Impulse load pattern applied at the free end of the beam.
# Test for small strain euler beam vibration in y direction
# An impulse load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 1e4
# Shear modulus (G) = 4e7
# Shear coefficient (k) = 1.0
# Cross-section area (A) = 0.01
# Iy = 1e-4 = Iz
# Length (L)= 4 m
# density (rho) = 1.0
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 6.4e6
# Therefore, the beam behaves like a Euler-Bernoulli beam.
# The theoretical first and third frequencies of this beam are:
# f1 = 1/(2 pi) * (3.5156/L^2) * sqrt(EI/rho)
# f2 = 6.268 f1
# This implies that the corresponding time period of this beam are 2.858 s and 0.455s
# The FEM solution for this beam with 10 element gives time periods of 2.856 s and 0.4505s with a time step of 0.01.
# A smaller time step is required to obtain a closer match for the lower time periods/higher frequencies.
# A higher time step of 0.05 is used in this test to reduce testing time.
# The time history from this analysis matches with that obtained from Abaqus.
# Values from the first few time steps are as follows:
# time disp_y vel_y accel_y
# 0 0.0 0.0 0.0
# 0.05 0.0016523559162602 0.066094236650407 2.6437694660163
# 0.1 0.0051691308901533 0.07457676230532 -2.3044684398197
# 0.15 0.0078956772343372 0.03448509146203 4.7008016060883
# 0.2 0.0096592517031463 0.03605788729033 -0.63788977295649
# 0.25 0.011069233444348 0.020341382357756 0.0092295756535376
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 4.0
dim = 1
nx = 10
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[./vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel<<<{"description": "Residual contribution to an ODE from a source functor acting at nodes.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
functor<<<{"description": "The forcing functor. A functor is any of the following: a variable, a functor material property, a function, a postprocessor or a number."}>>> = force
[../]
[]
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[./force]
type = PiecewiseLinear<<<{"description": "Linearly interpolates between pairs of x-y data", "href": "../../source/functions/PiecewiseLinear.html"}>>>
x<<<{"description": "The abscissa values"}>>> = '0.0 0.05 0.1 10.0'
y<<<{"description": "The ordinate values"}>>> = '0.0 0.01 0.0 0.0'
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
dt = 0.05
end_time = 5.0
timestep_tolerance = 1e-6
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[./inertial_force_x]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./inertial_force_y]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./inertial_force_z]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_x]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_y]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_z]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 0.01
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1e-4
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e4
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = -0.999875
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.01
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./density]
type = GenericConstantMaterial<<<{"description": "Declares material properties based on names and values prescribed by input parameters.", "href": "../../source/materials/GenericConstantMaterial.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
prop_names<<<{"description": "The names of the properties this material will have"}>>> = 'density'
prop_values<<<{"description": "The values associated with the named properties"}>>> = '1.0'
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = vel_y
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = accel_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]Results
For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha is given by: Therefore, the beam behaves like an Euler-Bernoulli beam. The displacement, velocity and acceleration, as the function of time, at the free end of the cantilever beam in MOOSE, are compared with the results from ABAQUS using the time step of 0.05 s, as shown in Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10.
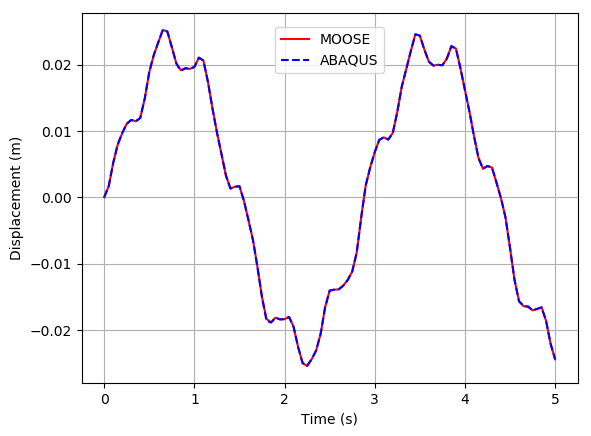
Figure 8: Displacement at the free end of the Euler beam.
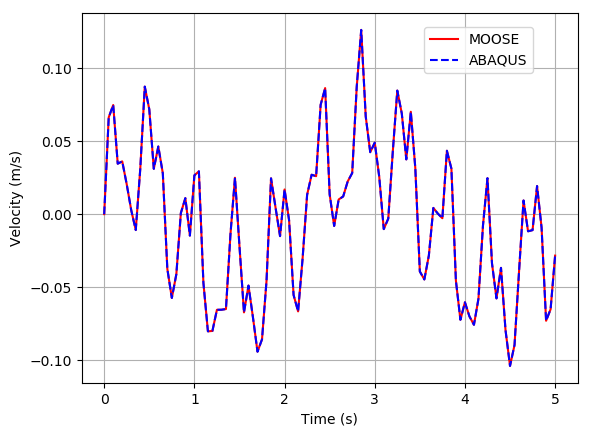
Figure 9: Velocity at the free end of the Euler beam.
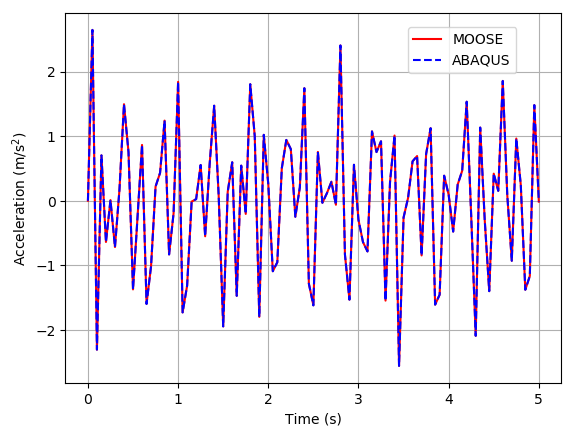
Figure 10: Acceleration at the free end of the Euler beam.
Small strain Timoshenko beam vibration
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam has a cross section area of 1 , moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 1 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 210 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, density of 1 kg/, shear modulus of 110 N/ and shear coefficient of 1. An impulse load with a peak value of 0.01 N at 0.0.005 s, as shown in Figure 11, is applied at the free end of the beam in Y direction. The Newmark time integration parameters used in the problem correspond to the Newmark's average acceleration method, i.e., beta=0.25 and gamma=0.5
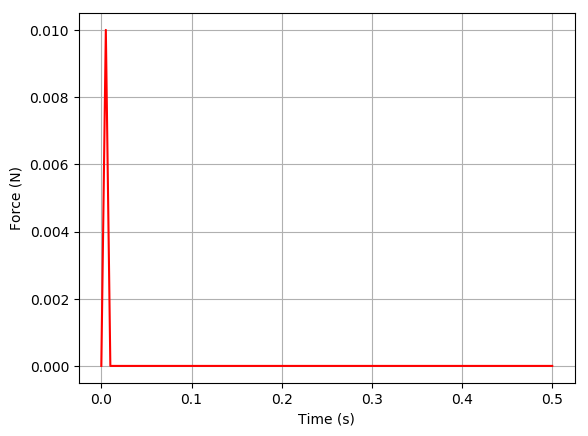
Figure 11: Impulse load pattern applied at the free end of the beam.
# Test for small strain Timoshenko beam vibration in y direction
# An impulse load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 2e4
# Shear modulus (G) = 1e4
# Shear coefficient (k) = 1.0
# Cross-section area (A) = 1.0
# Iy = 1.0 = Iz
# Length (L)= 4 m
# density (rho) = 1.0
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 8
# Therefore, the beam behaves like a Timoshenko beam.
# The FEM solution for this beam with 100 elements give first natural period of 0.2731s with a time step of 0.005.
# The acceleration, velocity and displacement time histories obtained from MOOSE matches with those obtained from ABAQUS.
# Values from the first few time steps are as follows:
# time disp_y vel_y accel_y
# 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
# 0.005 2.5473249455812e-05 0.010189299782325 4.0757199129299
# 0.01 5.3012872677486e-05 0.00082654950634483 -7.8208200233219
# 0.015 5.8611622914354e-05 0.0014129505884026 8.055380456145
# 0.02 6.766113649781e-05 0.0022068548449798 -7.7378187535141
# 0.025 7.8981810558437e-05 0.0023214147792709 7.7836427272305
# Note that the theoretical first frequency of the beam using Euler-Bernoulli theory is:
# f1 = 1/(2 pi) * (3.5156/L^2) * sqrt(EI/rho) = 4.9455
# This implies that the corresponding time period of this beam (under Euler-Bernoulli assumption) is 0.2022s.
# This shows that Euler-Bernoulli beam theory under-predicts the time period of a thick beam. In other words, the Euler-Bernoulli beam theory predicts a more compliant beam than reality for a thick beam.
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
xmin = 0
xmax = 4.0
nx = 100
dim = 1
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[./vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel<<<{"description": "Residual contribution to an ODE from a source functor acting at nodes.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
functor<<<{"description": "The forcing functor. A functor is any of the following: a variable, a functor material property, a function, a postprocessor or a number."}>>> = force
[../]
[]
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[./force]
type = PiecewiseLinear<<<{"description": "Linearly interpolates between pairs of x-y data", "href": "../../source/functions/PiecewiseLinear.html"}>>>
x<<<{"description": "The abscissa values"}>>> = '0.0 0.005 0.01 1.0'
y<<<{"description": "The ordinate values"}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0'
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
line_search = 'none'
nl_rel_tol = 1e-11
nl_abs_tol = 1e-11
start_time = 0.0
dt = 0.005
end_time = 0.5
timestep_tolerance = 1e-6
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[./inertial_force_x]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./inertial_force_y]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./inertial_force_z]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_x]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_y]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./inertial_force_rot_z]
type = InertialForceBeam<<<{"description": "Calculates the residual for the inertial force/moment and the contribution of mass dependent Rayleigh damping and HHT time integration scheme.", "href": "../../source/kernels/InertialForceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacement variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotational variables appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
velocities<<<{"description": "Translational velocity variables"}>>> = 'vel_x vel_y vel_z'
accelerations<<<{"description": "Translational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'accel_x accel_y accel_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "Rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "Rotational acceleration variables"}>>> = 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
area<<<{"description": "Variable containing cross-section area"}>>> = 1.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Variable containing second moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about y axis"}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "Variable containing first moment of area about z axis"}>>> = 0.0
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 2e4
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./density]
type = GenericConstantMaterial<<<{"description": "Declares material properties based on names and values prescribed by input parameters.", "href": "../../source/materials/GenericConstantMaterial.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
prop_names<<<{"description": "The names of the properties this material will have"}>>> = 'density'
prop_values<<<{"description": "The values associated with the named properties"}>>> = '1.0'
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = vel_y
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = accel_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]Results
For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha is given by: Therefore, the beam behaves like a Timoshenko beam. The displacement, velocity and acceleration, as the function of time, at the free end of the cantilever beam in MOOSE, are compared with the results from ABAQUS using the time step of 0.005 s, as shown in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14.
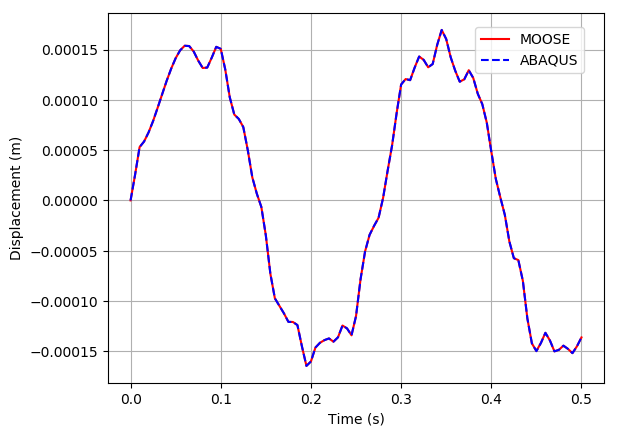
Figure 12: Displacement at the free end of the Timoshenko beam.
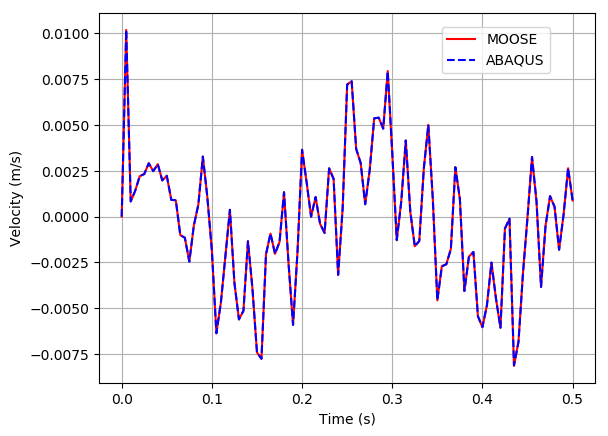
Figure 13: Velocity at the free end of the Timoshenko beam.
Figure 14: Acceleration at the free end of the Timoshenko beam.
Small strain massless beam vibration with a lumped mass
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam is massless with a lumped mass of 0.0189972 kgs at its free end. The beam has a moment of inertia of 110 about Y and Z axis, Young's modulus of elasticity of 110 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, shear modulus of 410 N/ and shear coefficient of 1. An impulse load with a peak value of 0.01 N at 0.1 s, as shown in Figure 15, is applied at the free end of the beam in Y direction. The Newmark time integration parameters used in the problem correspond to the Newmark's average acceleration method, i.e., beta=0.25 and gamma=0.5.
Figure 15: Impulse load pattern applied at the free end of the beam.
# Test for small strain euler beam vibration in y direction
# An impulse load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The beam is massless with a lumped mass at the end of the beam
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 1e4
# Shear modulus (G) = 4e7
# Shear coefficient (k) = 1.0
# Cross-section area (A) = 0.01
# Iy = 1e-4 = Iz
# Length (L)= 4 m
# mass (m) = 0.01899772
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 6.4e6
# Therefore, the beam behaves like a Euler-Bernoulli beam.
# The theoretical first frequency of this beam is:
# f1 = 1/(2 pi) * sqrt(3EI/(mL^3)) = 0.25
# This implies that the corresponding time period of this beam is 4s.
# The FEM solution for this beam with 10 element gives time periods of 4s with time step of 0.01s.
# A higher time step of 0.1 s is used in the test to reduce computational time.
# The time history from this analysis matches with that obtained from Abaqus.
# Values from the first few time steps are as follows:
# time disp_y vel_y accel_y
# 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
# 0.1 0.0013076435060869 0.026152870121738 0.52305740243477
# 0.2 0.0051984378734383 0.051663017225289 -0.01285446036375
# 0.3 0.010269120909367 0.049750643493289 -0.02539301427625
# 0.4 0.015087433925158 0.046615616822532 -0.037307519138892
# 0.5 0.019534963888307 0.042334982440433 -0.048305168503101
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 4.0
nx = 10
dim = 1
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[./vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel<<<{"description": "Residual contribution to an ODE from a source functor acting at nodes.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
functor<<<{"description": "The forcing functor. A functor is any of the following: a variable, a functor material property, a function, a postprocessor or a number."}>>> = force
[../]
[./x_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
[../]
[./y_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
[../]
[./z_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
[../]
[]
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[./force]
type = PiecewiseLinear<<<{"description": "Linearly interpolates between pairs of x-y data", "href": "../../source/functions/PiecewiseLinear.html"}>>>
x<<<{"description": "The abscissa values"}>>> = '0.0 0.1 0.2 10.0'
y<<<{"description": "The ordinate values"}>>> = '0.0 1e-2 0.0 0.0'
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-ksp_type -pc_type'
petsc_options_value = 'preonly lu'
dt = 0.1
end_time = 5.0
timestep_tolerance = 1e-6
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e4
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = -0.999875
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.01
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = vel_y
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = accel_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]Results
The displacement, velocity and acceleration, as the function of time, at the free end of the cantilever beam in MOOSE, are compared with the results from ABAQUS using the time step of 0.1 s, as shown in Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18.
Figure 16: Displacement at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass.
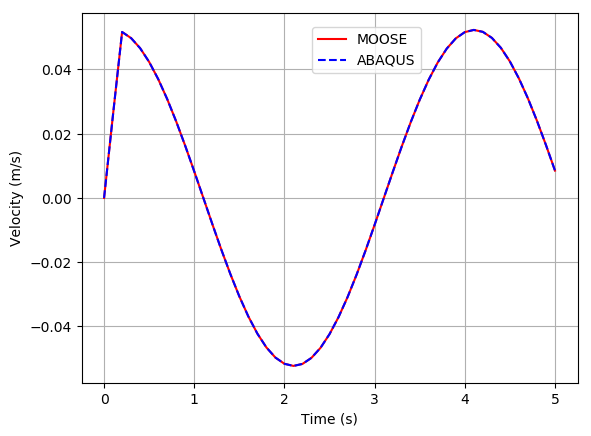
Figure 17: Velocity at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass.
Figure 18: Acceleration at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass.
Small strain massless beam damped vibration with a lumped mass having rotational moment of inertia
A 1D cantilever beam of 4 m is modeled using beam elements in MOOSE. The beam is massless with a lumped mass of 0.01899772 kgs at its free end whose moment of inertia about X, Y and Z axis is 0.2 ,0.1 and 0.1 , . The beam has a moment of inertia about Y and Z axis of 110 , Young's modulus of elasticity of 110 N/, poisson's ratio of -0.99, shear modulus of 410 N/ and shear coefficient of 1. An impulse load with a peak value of 0.01 N at 0.1 s as shown in Figure 19 is applied at the free end of the beam in Y direction. The Newmark time integration parameters used in the problem correspond to the Newmark's average acceleration method, i.e., beta=0.25 and gamma=0.5 and vibration is damping using the mass proportional coefficient eta=0.1.

Figure 19: Impulse load pattern applied at the free end of the beam.
# Test for small strain euler beam vibration in y direction
# An impulse load is applied at the end of a cantilever beam of length 4m.
# The beam is massless with a lumped mass at the end of the beam. The lumped
# mass also has a moment of inertia associated with it.
# The properties of the cantilever beam are as follows:
# Young's modulus (E) = 1e4
# Shear modulus (G) = 4e7
# Shear coefficient (k) = 1.0
# Cross-section area (A) = 0.01
# Iy = 1e-4 = Iz
# Length (L)= 4 m
# mass (m) = 0.01899772
# Moment of inertia of lumped mass:
# Ixx = 0.2
# Iyy = 0.1
# Izz = 0.1
# mass proportional damping coefficient (eta) = 0.1
# For this beam, the dimensionless parameter alpha = kAGL^2/EI = 6.4e6
# Therefore, the beam behaves like a Euler-Bernoulli beam.
# The displacement time history from this analysis matches with that obtained from Abaqus.
# Values from the first few time steps are as follows:
# time disp_y vel_y accel_y
# 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
# 0.1 0.001278249649738 0.025564992994761 0.51129985989521
# 0.2 0.0049813090917644 0.048496195845768 -0.052675802875074
# 0.3 0.0094704658873002 0.041286940064947 -0.091509312741339
# 0.4 0.013082280729802 0.03094935678508 -0.115242352856
# 0.5 0.015588313103503 0.019171290688959 -0.12031896906642
[Mesh<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Mesh/index.html"}>>>]
type = GeneratedMesh
dim = 1
nx = 10
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 4.0
displacements<<<{"description": "The variables corresponding to the x y z displacements of the mesh. If this is provided then the displacements will be taken into account during the computation. Creation of the displaced mesh can be suppressed even if this is set by setting 'use_displaced_mesh = false'."}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
[]
[Variables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Variables/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./disp_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxVariables<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxVariables/index.html"}>>>]
[./vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
order<<<{"description": "Specifies the order of the FE shape function to use for this variable (additional orders not listed are allowed)"}>>> = FIRST
family<<<{"description": "Specifies the family of FE shape functions to use for this variable"}>>> = LAGRANGE
[../]
[]
[AuxKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/AuxKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_x]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_x
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_x
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_x]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_x
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_y]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_y
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_y
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_y]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_y
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_accel_z]
type = NewmarkAccelAux<<<{"description": "Computes the current acceleration using the Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkAccelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_accel_z
displacement<<<{"description": "displacement variable"}>>> = rot_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = rot_vel_z
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.25
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[./rot_vel_z]
type = NewmarkVelAux<<<{"description": "Calculates the current velocity using Newmark method.", "href": "../../source/auxkernels/NewmarkVelAux.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this object applies to"}>>> = rot_vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = rot_accel_z
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark method"}>>> = 0.5
execute_on<<<{"description": "The list of flag(s) indicating when this object should be executed. For a description of each flag, see https://mooseframework.inl.gov/source/interfaces/SetupInterface.html."}>>> = timestep_end
[../]
[]
[BCs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/BCs/index.html"}>>>]
[./fixx1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixy1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixz1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr1]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr2]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[./fixr3]
type = DirichletBC<<<{"description": "Imposes the essential boundary condition $u=g$, where $g$ is a constant, controllable value.", "href": "../../source/bcs/DirichletBC.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundary IDs from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = left
value<<<{"description": "Value of the BC"}>>> = 0.0
[../]
[]
[NodalKernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/NodalKernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./force_y2]
type = UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel<<<{"description": "Residual contribution to an ODE from a source functor acting at nodes.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/UserForcingFunctorNodalKernel.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
functor<<<{"description": "The forcing functor. A functor is any of the following: a variable, a functor material property, a function, a postprocessor or a number."}>>> = force
[../]
[./x_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_x
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_x
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter for Rayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
[../]
[./y_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_y
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_y
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter for Rayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
[../]
[./z_inertial]
type = NodalTranslationalInertia<<<{"description": "Computes the inertial forces and mass proportional damping terms corresponding to nodal mass.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalTranslationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
velocity<<<{"description": "velocity variable"}>>> = vel_z
acceleration<<<{"description": "acceleration variable"}>>> = accel_z
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
mass<<<{"description": "Mass associated with the node"}>>> = 0.01899772
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter for Rayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
[../]
[./rot_x_inertial]
type = NodalRotationalInertia<<<{"description": "Calculates the inertial torques and inertia proportional damping corresponding to the nodal rotational inertia.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalRotationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
rotations<<<{"description": "rotational displacement variables"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "rotational acceleration variables"}>>>= 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
Ixx<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the x direction."}>>> = 2e-1
Iyy<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the y direction."}>>> = 1e-1
Izz<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the z direction."}>>> = 1e-1
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter forRayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this nodalkernel acts in. (0 for rot_x, 1 for rot_y, and 2 for rot_z)."}>>> = 0
[../]
[./rot_y_inertial]
type = NodalRotationalInertia<<<{"description": "Calculates the inertial torques and inertia proportional damping corresponding to the nodal rotational inertia.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalRotationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
rotations<<<{"description": "rotational displacement variables"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "rotational acceleration variables"}>>>= 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
Ixx<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the x direction."}>>> = 2e-1
Iyy<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the y direction."}>>> = 1e-1
Izz<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the z direction."}>>> = 1e-1
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter forRayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this nodalkernel acts in. (0 for rot_x, 1 for rot_y, and 2 for rot_z)."}>>> = 1
[../]
[./rot_z_inertial]
type = NodalRotationalInertia<<<{"description": "Calculates the inertial torques and inertia proportional damping corresponding to the nodal rotational inertia.", "href": "../../source/nodalkernels/NodalRotationalInertia.html"}>>>
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
rotations<<<{"description": "rotational displacement variables"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
rotational_velocities<<<{"description": "rotational velocity variables"}>>> = 'rot_vel_x rot_vel_y rot_vel_z'
rotational_accelerations<<<{"description": "rotational acceleration variables"}>>>= 'rot_accel_x rot_accel_y rot_accel_z'
boundary<<<{"description": "The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies"}>>> = right
beta<<<{"description": "beta parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.25
gamma<<<{"description": "gamma parameter for Newmark Time integration"}>>> = 0.5
Ixx<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the x direction."}>>> = 2e-1
Iyy<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the y direction."}>>> = 1e-1
Izz<<<{"description": "Moment of inertia in the z direction."}>>> = 1e-1
eta<<<{"description": "Constant real number defining the eta parameter forRayleigh damping."}>>> = 0.1
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this nodalkernel acts in. (0 for rot_x, 1 for rot_y, and 2 for rot_z)."}>>> = 2
[../]
[]
[Functions<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Functions/index.html"}>>>]
[./force]
type = PiecewiseLinear<<<{"description": "Linearly interpolates between pairs of x-y data", "href": "../../source/functions/PiecewiseLinear.html"}>>>
x<<<{"description": "The abscissa values"}>>> = '0.0 0.1 0.2 10.0'
y<<<{"description": "The ordinate values"}>>> = '0.0 1e-2 0.0 0.0'
[../]
[]
[Preconditioning<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Preconditioning/index.html"}>>>]
[./smp]
type = SMP<<<{"description": "Single matrix preconditioner (SMP) builds a preconditioner using user defined off-diagonal parts of the Jacobian.", "href": "../../source/preconditioners/SingleMatrixPreconditioner.html"}>>>
full<<<{"description": "Set to true if you want the full set of couplings between variables simply for convenience so you don't have to set every off_diag_row and off_diag_column combination."}>>> = true
[../]
[]
[Executioner<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Executioner/index.html"}>>>]
type = Transient
solve_type = NEWTON
petsc_options_iname = '-ksp_type -pc_type'
petsc_options_value = 'preonly lu'
dt = 0.1
end_time = 5.0
timestep_tolerance = 1e-6
[]
[Kernels<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Kernels/index.html"}>>>]
[./solid_disp_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 0
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./solid_disp_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 1
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./solid_disp_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 2
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = disp_z
[../]
[./solid_rot_x]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 3
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_x
[../]
[./solid_rot_y]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 4
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_y
[../]
[./solid_rot_z]
type = StressDivergenceBeam<<<{"description": "Quasi-static and dynamic stress divergence kernel for Beam element", "href": "../../source/kernels/StressDivergenceBeam.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
component<<<{"description": "An integer corresponding to the direction the variable this kernel acts in. (0 for disp_x, 1 for disp_y, 2 for disp_z, 3 for rot_x, 4 for rot_y and 5 for rot_z)"}>>> = 5
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this residual object operates on"}>>> = rot_z
[../]
[]
[Materials<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Materials/index.html"}>>>]
[./elasticity]
type = ComputeElasticityBeam<<<{"description": "Computes the equivalent of the elasticity tensor for the beam element, which are vectors of material translational and flexural stiffness.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeElasticityBeam.html"}>>>
youngs_modulus<<<{"description": "Young's modulus of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e4
poissons_ratio<<<{"description": "Poisson's ratio of the material. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = -0.999875
shear_coefficient<<<{"description": "Scale factor for the shear modulus. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[./strain]
type = ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain<<<{"description": "Compute a infinitesimal/large strain increment for the beam.", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeIncrementalBeamStrain.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = '0'
displacements<<<{"description": "The displacements appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'disp_x disp_y disp_z'
rotations<<<{"description": "The rotations appropriate for the simulation geometry and coordinate system"}>>> = 'rot_x rot_y rot_z'
area<<<{"description": "Cross-section area of the beam. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.01
Ay<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Az<<<{"description": "First moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 0.0
Iy<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about y axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
Iz<<<{"description": "Second moment of area of the beam about z axis. Can be supplied as either a number or a variable name."}>>> = 1.0e-4
y_orientation<<<{"description": "Orientation of the y direction along with Iyy is provided. This should be perpendicular to the axis of the beam."}>>> = '0.0 1.0 0.0'
[../]
[./stress]
type = ComputeBeamResultants<<<{"description": "Compute forces and moments using elasticity", "href": "../../source/materials/ComputeBeamResultants.html"}>>>
block<<<{"description": "The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied"}>>> = 0
[../]
[]
[Postprocessors<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Postprocessors/index.html"}>>>]
[./disp_x]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_x
[../]
[./disp_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = disp_y
[../]
[./vel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = vel_y
[../]
[./accel_y]
type = PointValue<<<{"description": "Compute the value of a variable at a specified location", "href": "../../source/postprocessors/PointValue.html"}>>>
point<<<{"description": "The physical point where the solution will be evaluated."}>>> = '4.0 0.0 0.0'
variable<<<{"description": "The name of the variable that this postprocessor operates on."}>>> = accel_y
[../]
[]
[Outputs<<<{"href": "../../syntax/Outputs/index.html"}>>>]
exodus<<<{"description": "Output the results using the default settings for Exodus output."}>>> = true
csv<<<{"description": "Output the scalar variable and postprocessors to a *.csv file using the default CSV output."}>>> = true
perf_graph<<<{"description": "Enable printing of the performance graph to the screen (Console)"}>>> = true
[]Results
The displacement, velocity and acceleration, as the function of time, at the free end of the cantilever beam in MOOSE, are compared with the results from ABAQUS using the time step of 0.1 s, as shown in Figure 20, Figure 21 and Figure 22.
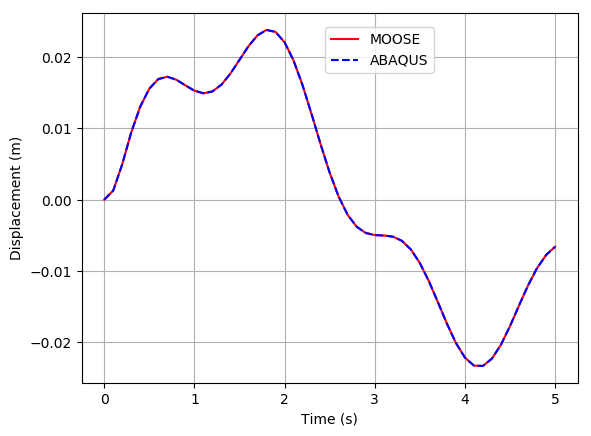
Figure 20: Displacement at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass having rotational moment of inertia.
Figure 21: Velocity at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass having rotational moment of inertia.
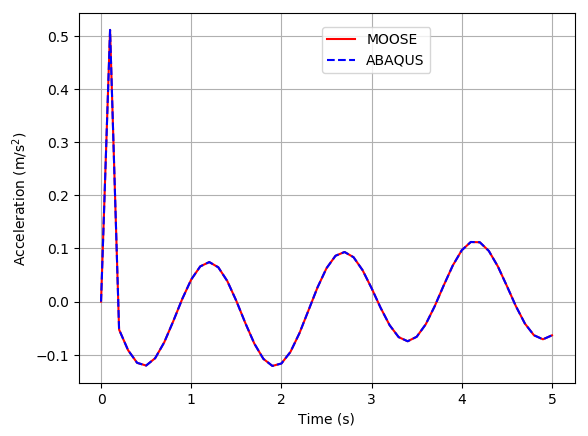
Figure 22: Acceleration at the free end of the massless beam with lumped mass having rotational moment of inertia.
References
- K. E. BISSHOPP and D. C. DRUCKER.
Large deflection of cantilever beams.
Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 3(3):272–275, 1945.
URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/43633516.[BibTeX]